OpenTelemetry is a vendor-agnostic instrumentation library under CNCF. It can be used to instrument your Python applications to generate telemetry data. Let's learn how it works and see how to visualize that data with SigNoz.
The cost of a millisecond.
TABB Group, a financial services industry research firm, estimates that if a broker's electronic trading platform is 5 milliseconds behind the competition, it could cost $4 million in revenue per millisecond.
The cost of latency is too high in the financial services industry, and the same is true for almost any software-based business today. Half a second is enough to kill user satisfaction to a point where they abandon an app's service.
Capturing and analyzing data about your production environment is critical. You need to proactively solve stability and performance issues in your web application to avoid system failures and ensure a smooth user experience.
In a microservices architecture, the challenge is to solve availability and performance issues quickly. You need observability for your applications. And, observability is powered with telemetry data.
What is OpenTelemetry?
OpenTelemetry emerged as a single project after the merging of OpenCensus(from Google) and OpenTracing(from Uber) into a single project. The project aims to make telemetry data(logs, metrics, and traces) a built-in feature of cloud-native software applications.
OpenTelemetry has laguage-specific implementation for generating telemetry data which includes OpenTelemetry Python libraries.
You can check out the current releases of opentelemetry-python.
OpenTelemetry only generates telemetry data and lets you decide where to send your data for analysis and visualization.
In this article, we will use SigNoz as a backend. SigNoz is an open-source APM tool that can be used for both metrics and distributed tracing.
Let's get started and see how to use OpenTelemetry for a Flask application.
Running a Python application with OpenTelemetry
OpenTelemetry is a set of tools, APIs, and SDKs used to instrument applications to create and manage telemetry data(logs, metrics, and traces).
Setting up SigNoz
You need a backend to which you can send the collected data for monitoring and visualization. SigNoz is an OpenTelemetry-native APM that is well-suited for visualizing OpenTelemetry data.

SigNoz cloud is the easiest way to run SigNoz. You can sign up here for a free account and get 30 days of unlimited access to all features.
You can also install and self-host SigNoz yourself. Check out the docs for installing self-host SigNoz.
Instrumenting a sample Python application with OpenTelemetry
Prerequisites
- Python 3.8 or newer
Download the latest version of Python.
MongoDB
If you already have MongoDB services running on your system, you can skip this step.Below are the download links for different OS:
MacOS
Linux
Windows
UbuntuOn MacOS the installation is done using Homebrew's brew package manager. Once the installation is done, don't forget to start MongoDB services using
brew services start mongodb/brew/mongodb-community@x.xon your macOS terminal where x being the mongodb version.
Step 1. Running sample Flask app
We will be using the Flask app at this Github repo. All the required OpenTelemetry packages are contained within the requirements.txt file.
git clone https://github.com/SigNoz/sample-flask-app.git
cd sample-flask-app
It’s a good practice to create virtual environments for running Python apps, so we will be using a virtual python environment for this sample Flask app.
Create a Virtual Environment
python3 -m venv .venv
source .venv/bin/activate
Check if the app is running
python3 app.py
You can now access the UI of the app on your local host: http://localhost:5002/
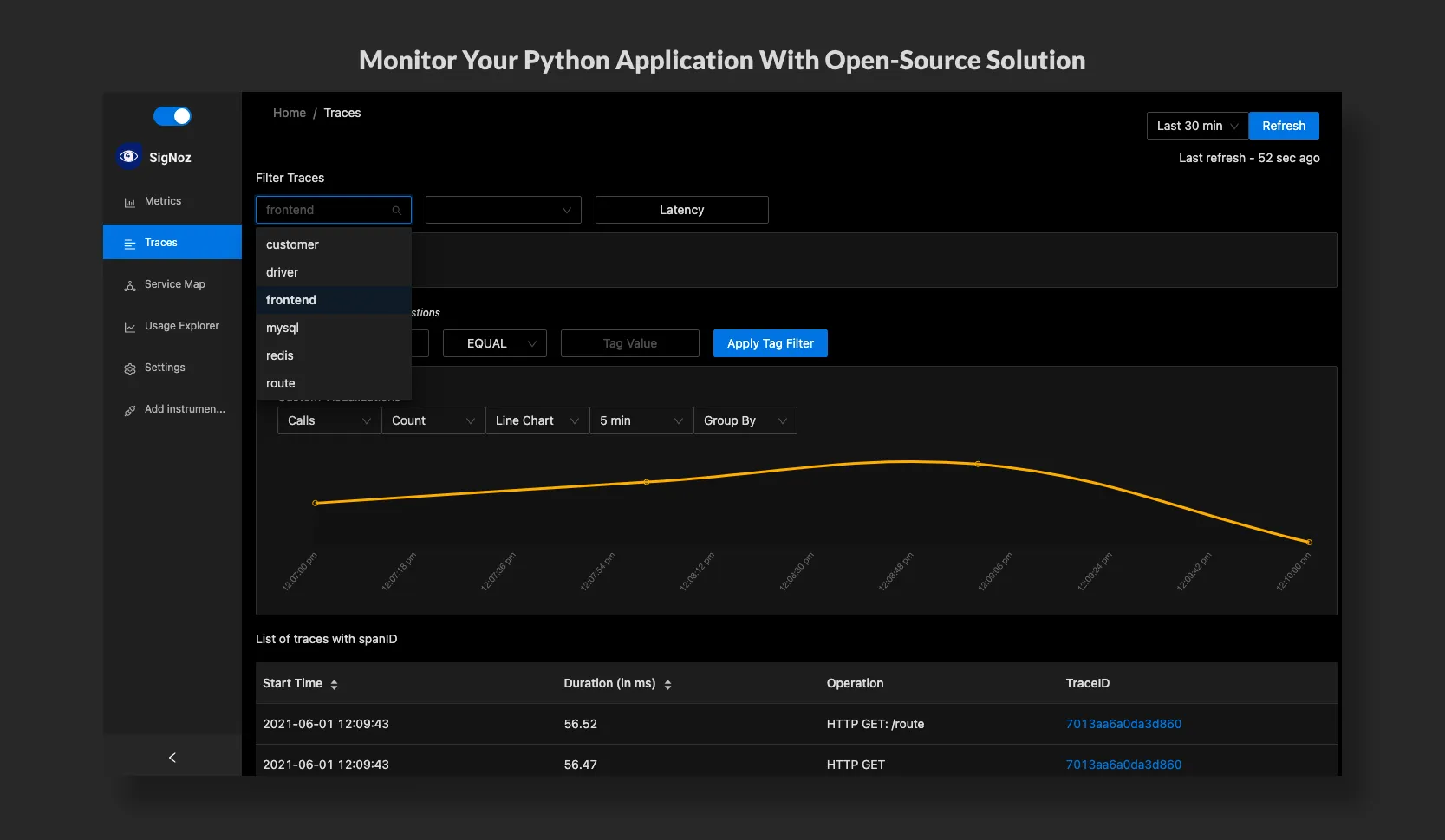
To capture data with OpenTelemetry, you need to configure some environment variables and run the app with OpenTelemetry packages. Once you ensure your app is running, stop the app with ctrl + c on a mac. Now, let us instrument the sample app with OpenTelemetry packages.
Step 2. Run instructions for sending data to SigNoz
Your app folder contains a file called requirements.txt. This file contains all the necessary commands to set up OpenTelemetry Python instrumentation. All the mandatory packages required to start the instrumentation are installed with the help of this file. Make sure your path is updated to the root directory of your sample app and run the following command:
python -m pip install -r requirements.txt
The requirements.txt file contains all the necessary OpenTelemetry Python packages needed for instrumentation. In order to install those packages, run the following command:
The opentelemetry-exporter-otlp is a convenience wrapper package to install all OTLP exporters. Currently, it installs:
- opentelemetry-exporter-otlp-proto-http
- opentelemetry-exporter-otlp-proto-grpc
- (soon) opentelemetry-exporter-otlp-json-http
The opentelemetry-exporter-otlp-proto-grpc package installs the gRPC exporter which depends on the grpcio package. The installation of grpcio may fail on some platforms for various reasons. If you run into such issues, or you don't want to use gRPC, you can install the HTTP exporter instead by installing the opentelemetry-exporter-otlp-proto-http package. You need to set the OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_PROTOCOL environment variable to http/protobuf to use the HTTP exporter.
If it hangs while installing grpcio during pip3 install opentelemetry-exporter-otlp then follow below steps as suggested in this stackoverflow link.
- pip3 install --upgrade pip
- python3 -m pip install --upgrade setuptools
- pip3 install --no-cache-dir --force-reinstall -Iv grpcio
Step 3. Install application specific packages
This step is required to install packages specific to the application. Make sure to run this command in the root directory of your installed application. This command figures out which instrumentation packages the user might want to install and installs it for them:
opentelemetry-bootstrap --action=install
Please make sure that you have installed all the dependencies of your application before running the above command. The command will not install instrumentation for the dependencies which are not installed.
Step 4. Configure environment variables to run app and send data to SigNoz
You're almost done. In the last step, you just need to configure a few environment variables for your OTLP exporters. Environment variables that need to be configured:
OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES=service.name=<service_name> \
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT="https://ingest.{region}.signoz.cloud:443" \
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS="signoz-ingestion-key=SIGNOZ_INGESTION_KEY" \
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_PROTOCOL=grpc \
opentelemetry-instrument <your_run_command>
<service_name>is the name of the service you want<your_run_command>can be python3 app.py or flask run- Replace SIGNOZ_INGESTION_KEY with the api token provided by SigNoz. You can find it in the email sent by SigNoz with your cloud account details.
You will be able to get ingestion details in SigNoz cloud account under settings --> ingestion settings.

Don’t run app in reloader/hot-reload mode as it breaks instrumentation. For example, if you use --reload or reload=True, it enables the reloader mode which breaks OpenTelemetry isntrumentation.
OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES=service.name=sample-flask-app \
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT="https://ingest.{region}.signoz.cloud:443" \
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS="signoz-ingestion-key=SIGNOZ_INGESTION_KEY" \
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_PROTOCOL=grpc \
opentelemetry-instrument python app.py
And, congratulations! You have instrumented your sample Flask app. You can check if your app is running or not by hitting the endpoint at http://localhost:5002/.
You need to interact with the application to generate some monitoring data.
Below you can find your sample-flask-app in the list of applications being monitored on SigNoz dashboard.
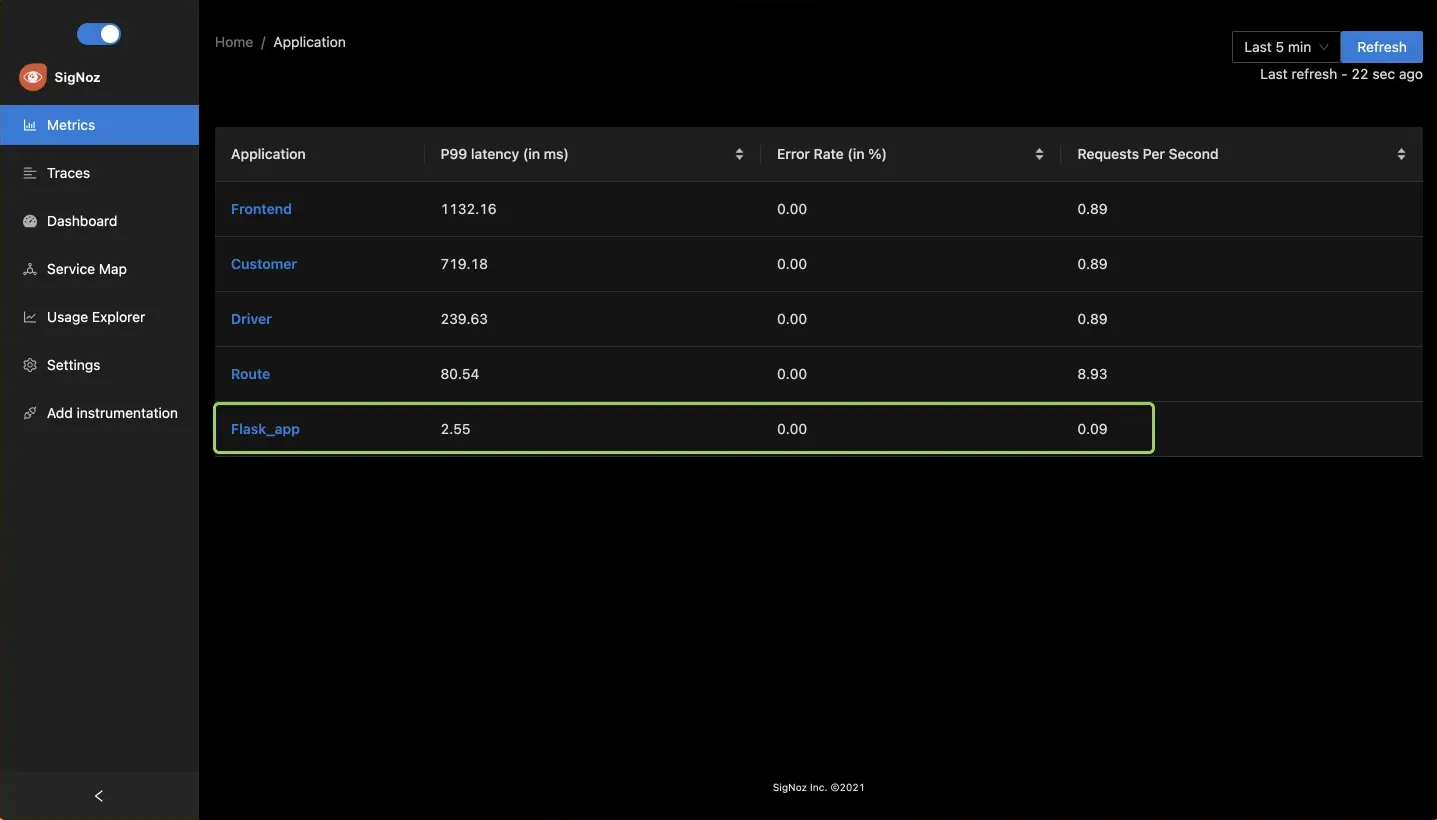
Troubleshooting
The debug mode can break instrumentation from happening because it enables a reloader. To run instrumentation while the debug mode is enabled, set the use_reloader option to False:
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=5002, debug=True, use_reloader=False)
If you face any problem in instrumenting with OpenTelemetry, refer to these docs.
Metrics and Traces of the Python application
SigNoz makes it easy to visualize metrics and traces captured through OpenTelemetry instrumentation.
SigNoz comes with out of box RED metrics charts and visualization. RED metrics stands for:
- Rate of requests
- Error rate of requests
- Duration taken by requests
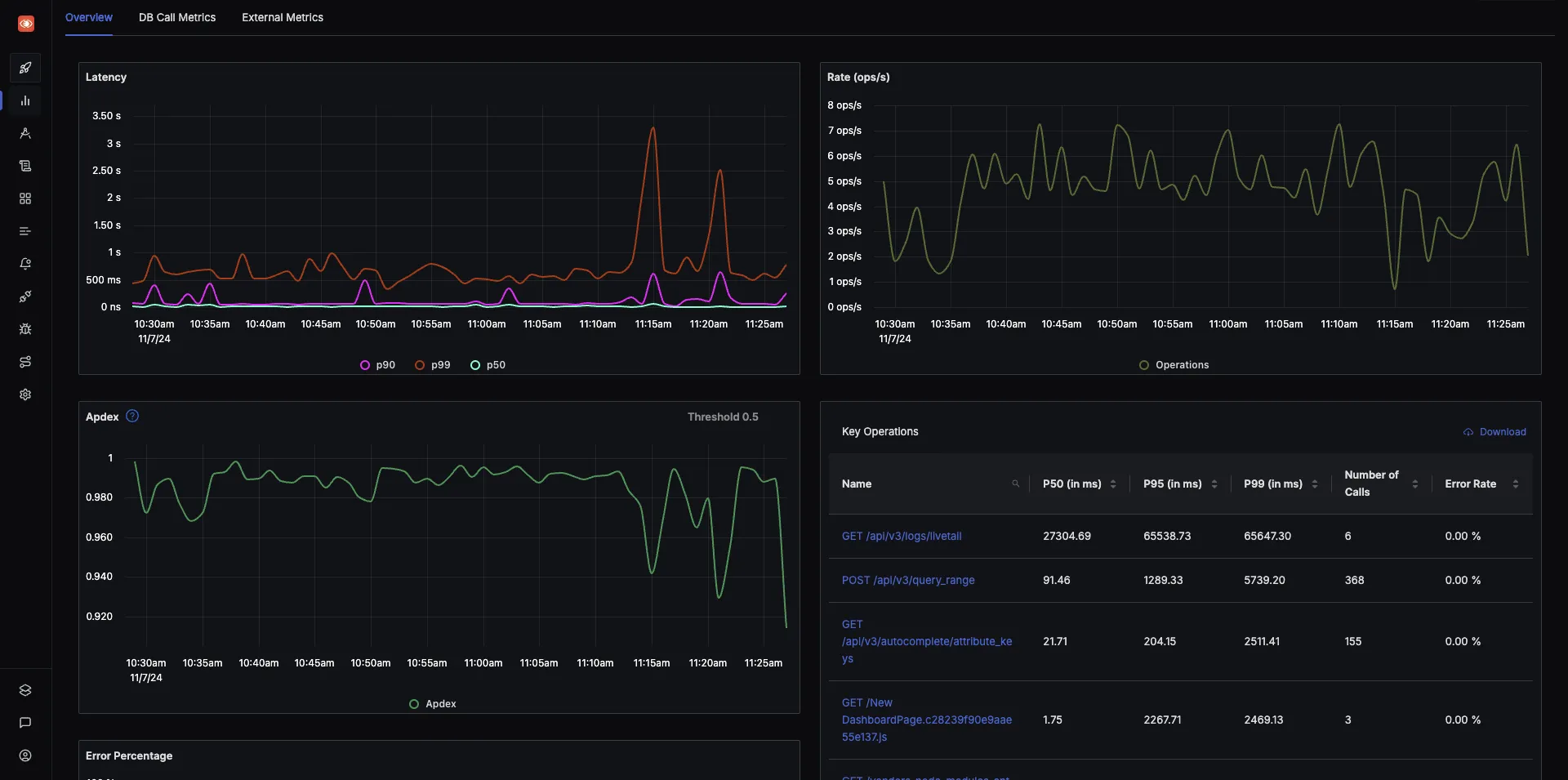
You can then choose a particular timestamp where latency is high to drill down to traces around that timestamp.

You can use flamegraphs to exactly identify the issue causing the latency.
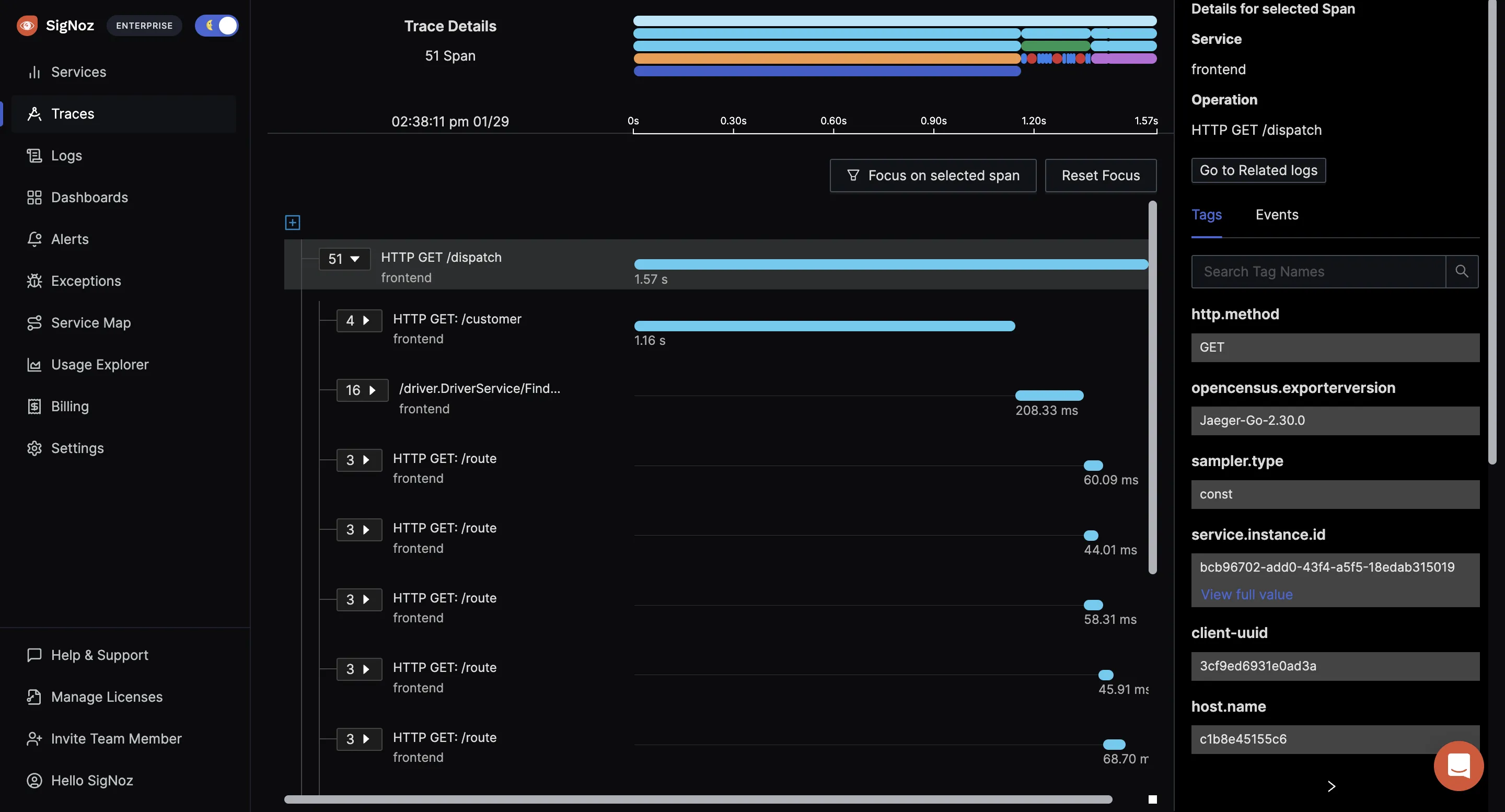
Conclusion
OpenTelemetry makes it very convenient to instrument your Python application. You can then use an open-source APM tool like SigNoz to analyze the performance of your app. As SigNoz offers a full-stack observability tool, you don't have to use multiple tools for your monitoring needs.
You can try out SigNoz by visiting its GitHub repo 👇
If you have any questions or need any help in setting things up, join our slack community and ping us in #support channel.
If you want to read more about SigNoz 👇
Golang Application Performance Monitoring with SigNoz
Nodejs Application Performance Monitoring with SigNoz




